Fundamentals of Azure for AI Applications
Core Services of Azure for AI
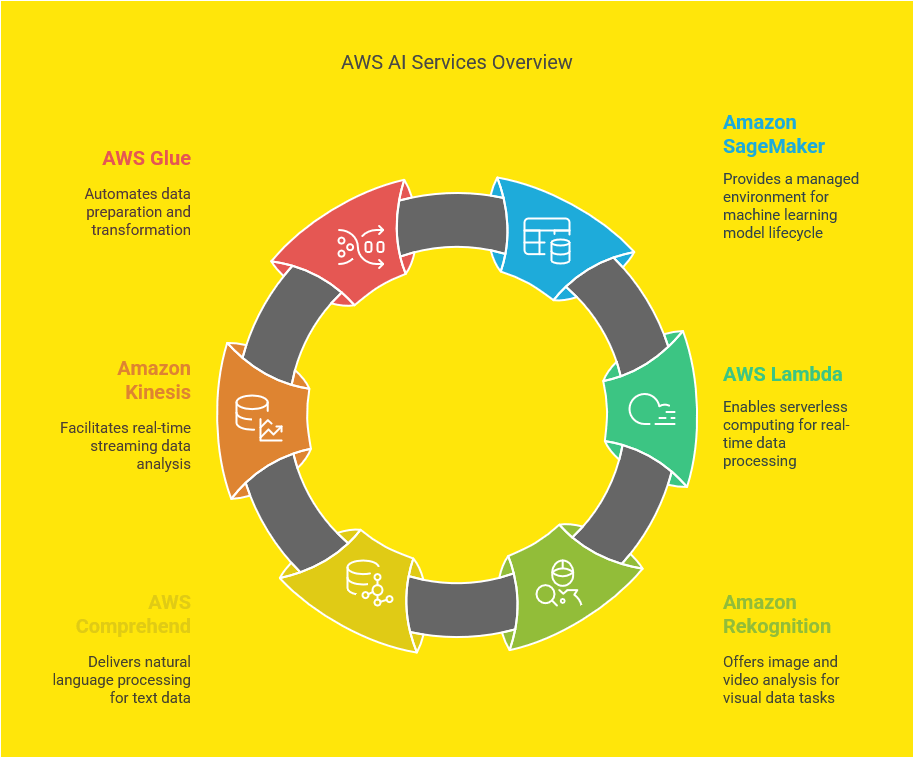
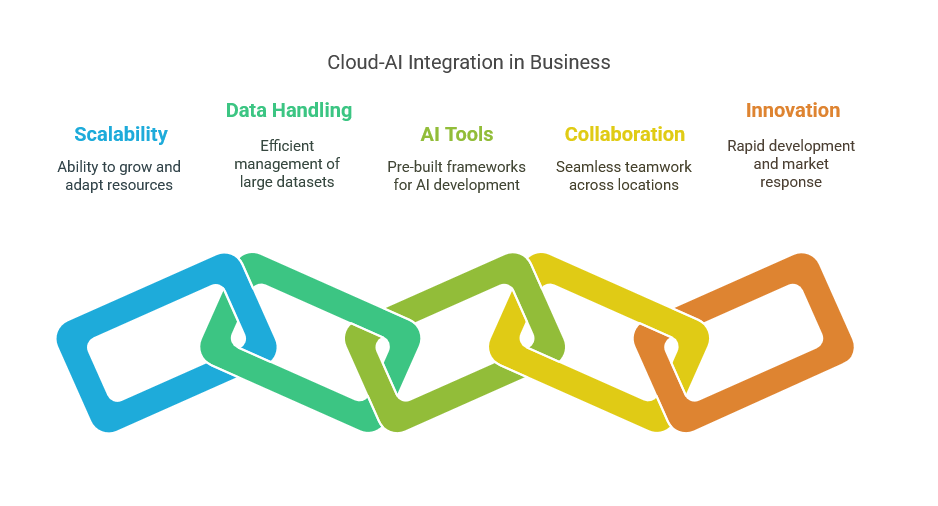
Azure provides a comprehensive suite of core services designed to facilitate the development, deployment, and management of artificial intelligence (AI) applications. Among these, Azure Machine Learning stands out as a powerful platform that enables IT professionals to build, train, and deploy machine learning models at scale. With features like automated machine learning, model interpretability, and robust collaboration tools, Azure Machine Learning caters to a wide range of use cases, from predictive analytics to natural language processing. This service empowers businesses to harness their data effectively and transform it into actionable insights, driving innovation and efficiency in their operations.
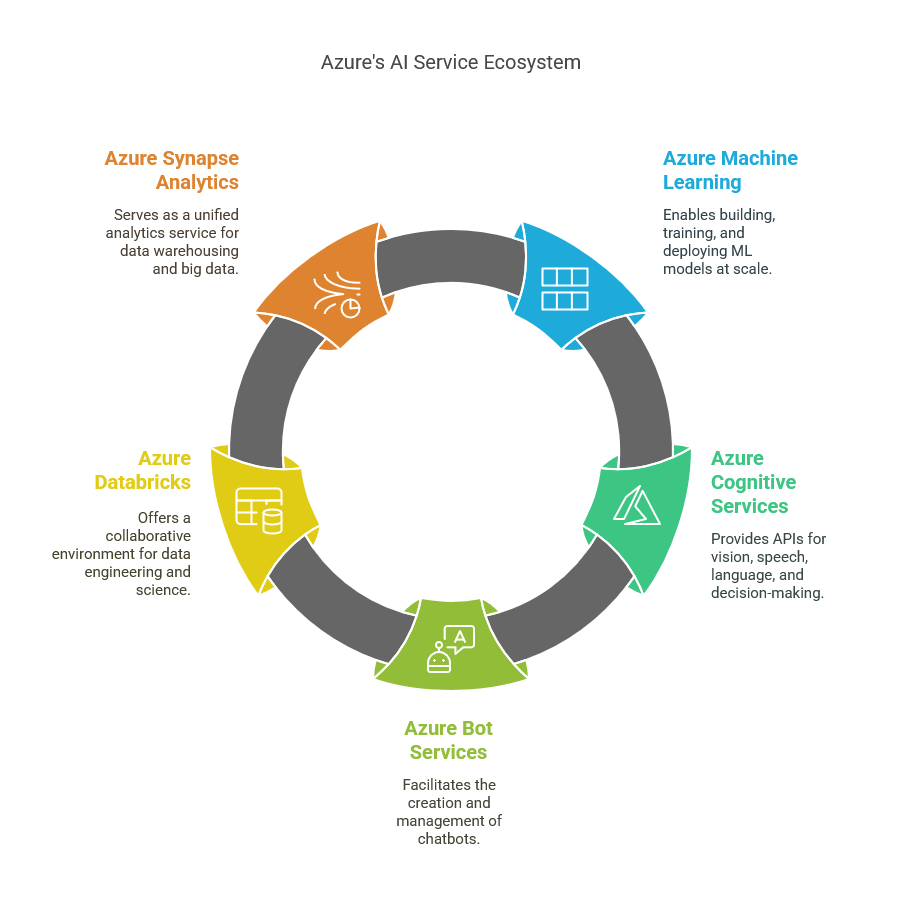
Another key service is Azure Cognitive Services, which offers a set of pre-built APIs that allow developers to integrate advanced AI capabilities into their applications without needing deep expertise in machine learning. These services encompass vision, speech, language, and decision-making functionalities, making it easier for organizations to enhance user experiences and automate processes. For instance, the Computer Vision API can analyze images and extract information, while the Speech Service enables real-time translation and transcription. By leveraging these cognitive services, IT professionals can quickly build intelligent applications that respond to user needs in real time.
Azure Bot Services is also essential for organizations looking to implement conversational AI solutions. This service allows developers to create and manage chatbots that can engage users across various channels, including websites, social media, and messaging platforms. The integration of natural language understanding through the Language Understanding (LUIS) service enhances the bots’ ability to comprehend user intents and respond appropriately. By utilizing Azure Bot Services, businesses can streamline customer interactions, reduce operational costs, and improve service delivery, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction.
In addition to these core services, Azure Databricks provides a collaborative environment for data engineering and data science. Built on Apache Spark, Databricks simplifies big data processing and enables teams to work together on AI projects seamlessly. By combining data storage, processing, and analytics capabilities, Databricks helps organizations unlock the full potential of their data, driving better decision-making and fostering innovation. IT professionals can leverage this platform to accelerate the development of AI models, ensuring they are built on accurate and up-to-date data.
Lastly, Azure Synapse Analytics serves as a unified analytics service that brings together big data and data warehousing. This service allows IT professionals to analyze vast amounts of data quickly and derive insights that can inform business strategies. With its integration of machine learning capabilities and support for real-time analytics, Azure Synapse Analytics empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions efficiently. Together, these core services of Azure create a robust ecosystem that enables IT professionals to architect AI solutions that drive business automation and enhance operational efficiency across various industries.
Data Management with Azure
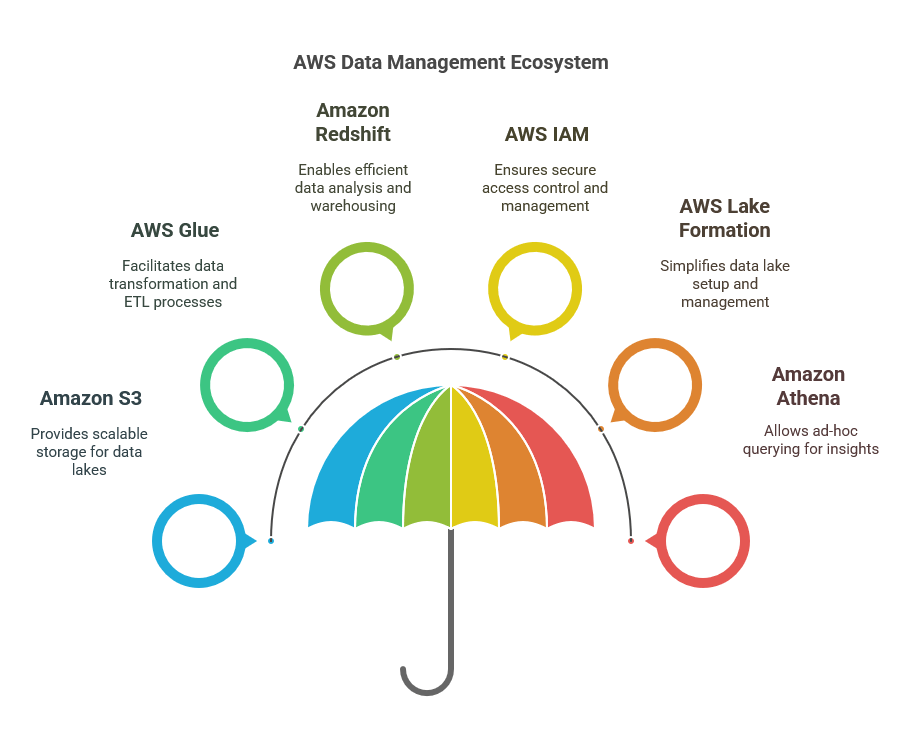
Data management is a cornerstone of effective business automation, and Azure provides a robust framework for handling data in a secure, efficient, and scalable manner. IT professionals engaged in architecting AI solutions can leverage Azure’s extensive database services, including Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB, and Azure Data Lake Storage. Each service is designed to meet specific needs, from relational data management to unstructured data processing, enabling businesses to choose the right tool for their unique requirements. This versatility is crucial in an era where data-driven decision-making is paramount.
Azure SQL Database offers a fully managed relational database service that simplifies the management of data while maintaining high availability and performance. It supports advanced features such as automated backups, scaling, and built-in intelligence, allowing IT professionals to focus on application development rather than database maintenance. Moreover, its compatibility with SQL Server means that organizations can easily migrate existing applications to the cloud without significant rewrites. This seamless transition not only reduces downtime but also enhances the overall agility of business operations.
For applications requiring global distribution and low-latency access, Azure Cosmos DB stands out as a multi-model database service. It supports various data models, including key-value, document, and graph formats, making it an ideal choice for diverse workloads. With its ability to replicate data across multiple regions with ease, IT professionals can ensure that applications remain responsive regardless of user location. The automatic scaling feature of Cosmos DB further optimizes performance and cost, adapting to changing workloads without manual intervention, which is instrumental for businesses aiming to meet fluctuating demands.
Azure Data Lake Storage is another critical component of Azure’s data management ecosystem, particularly for organizations dealing with large volumes of unstructured data. It provides a scalable and secure repository for big data analytics, supporting various data processing frameworks like Apache Spark and Hadoop. This capability allows IT professionals to harness the full potential of their data, transforming raw information into actionable insights. By integrating data from multiple sources into a single platform, organizations can streamline their analytics processes, facilitating more informed decision-making and enhancing operational efficiency.
In conclusion, effective data management with Azure is integral to successfully architecting AI solutions for business automation. By utilizing Azure’s diverse array of data services, IT professionals can create a cohesive data strategy that aligns with organizational goals. Emphasizing scalability, security, and performance, Azure empowers businesses to not only manage their data effectively but also to leverage it as a strategic asset in their automation efforts. As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of digital transformation, a solid foundation in data management will be essential for driving innovation and achieving competitive advantage.
Security and Compliance in Azure
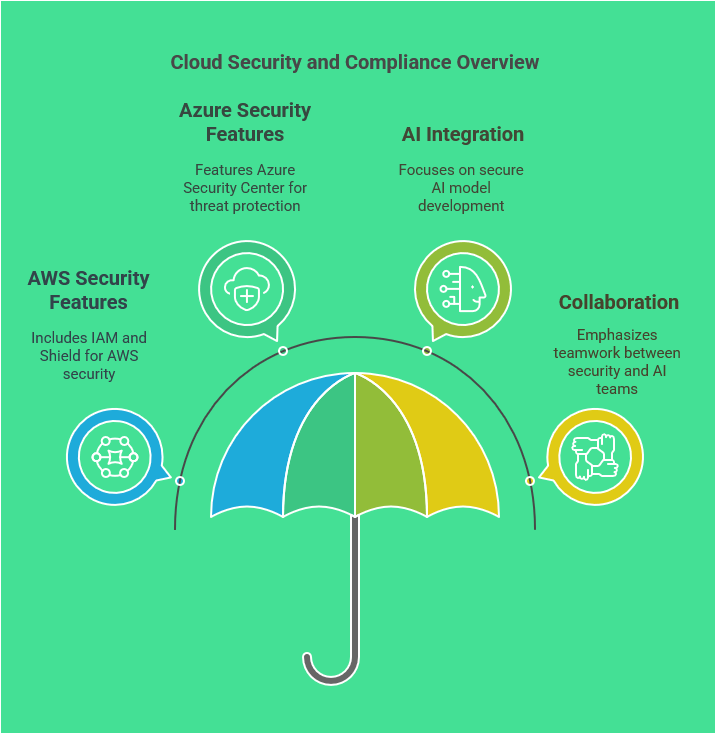
In the realm of cloud computing, security and compliance are paramount, especially when leveraging platforms like Azure to architect AI-driven business automation solutions. IT professionals must prioritize these elements to build trust and ensure the integrity of their applications. Azure provides a robust framework of security features, tools, and compliance certifications that can help organizations safeguard their data while adhering to regulatory requirements. Understanding these resources is essential for effectively managing risk and ensuring the resilience of business applications.
One of Azure’s most significant advantages is its comprehensive security model, which encompasses identity management, access control, data protection, and threat mitigation. Azure Active Directory plays a crucial role in managing user identities and access rights, enabling granular control over who can access which resources. This identity-centric approach not only enhances security but also simplifies compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. IT professionals should leverage Azure’s security tools to implement multi-factor authentication and conditional access policies, ensuring that only authorized users can interact with sensitive business applications.
Data protection in Azure is facilitated by a variety of built-in encryption and monitoring services. Both data at rest and in transit can be secured through Azure’s encryption capabilities, which safeguard sensitive information against unauthorized access. Additionally, Azure Security Center provides continuous security assessments and recommendations, allowing organizations to maintain a proactive posture against potential threats. IT professionals must adopt these tools to ensure that their AI-driven applications not only meet security standards but also align with best practices in data governance and protection.
Compliance is a multifaceted challenge, particularly for organizations operating in regulated industries. Azure addresses this through a comprehensive compliance framework that includes a wide array of certifications and attestations. Azure’s Compliance Manager allows IT teams to assess their compliance posture and manage risks effectively. By staying informed about evolving regulations and leveraging Azure’s compliance tools, IT professionals can ensure that their business automation solutions not only meet legal requirements but are also aligned with industry standards, thereby fostering greater stakeholder confidence.
In conclusion, security and compliance in Azure are integral to the successful architecting of AI-powered business applications. By harnessing the platform’s security features, data protection mechanisms, and compliance tools, IT professionals can build resilient and trustworthy solutions. As the landscape of business automation continues to evolve, maintaining a strong focus on these aspects will be crucial for organizations looking to innovate while safeguarding their most valuable asset: data. Embracing Azure’s capabilities will empower IT teams to navigate the complex regulatory environment confidently and effectively.