Service-Oriented Architecture in E‑Commerce: Core Business Modules
In the rapidly evolving world of online retail, building a scalable, maintainable, and flexible system is critical for staying competitive. Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) offers a proven approach by decomposing a monolithic application into a collection of loosely coupled services. Each service represents a specific business capability, communicates over well-defined interfaces, and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. Below, we examine the essential SOA-based modules for an e‑commerce company, detailing their responsibilities, interactions, and best practices.
=========>
🚨 eCommerce IT Professionals — Are You Ready to Stay Relevant in the AI Era?
- If you’re still working with legacy service-oriented systems, it’s time to rethink your future. The world of eCommerce is moving fast — and AI agentic applications are leading the charge.
🎯 That’s why I’m hosting a powerful upskilling session: - 🔹 “Upskill to AI Agentic Design for Legacy eCommerce Professionals”
💡 Why You Need to Upgrade: - ✅ Legacy SO architectures can’t meet the demands of modern commerce
✅ AI agents enable intelligent, adaptive, and scalable applications
✅ Companies are shifting to AI-first systems — fast
✅ Upskilling now protects your career from stagnation
✅ Learn to design the next-gen systems driving eCommerce innovation
For details follow:
https://lnkd.in/gQDvmcdz
1. Customer Management Service
Responsibilities:
- Store and manage customer profiles, registration, authentication, and authorization.
- Handle user preferences, address books, and communication consents (email/SMS opt‑in).
- Provide single sign-on (SSO) integration and federated identity (OAuth, SAML).
Key Features & Benefits:
- Centralized user identity ensures consistent authentication across all modules.
- Supports multi‑channel personalization by exposing APIs for profile retrieval.
- Enhances security with token-based authentication and role-based access control.
Integration Points:
- Order Management Service consumes customer shipping/billing data.
- Marketing & Promotions Service uses preferences for targeted campaigns.
- Analytics Service aggregates customer behavior for insights.
Customer Management forms the backbone of a secure, personalized shopper experience by abstracting identity operations into a standalone service(Oracle).
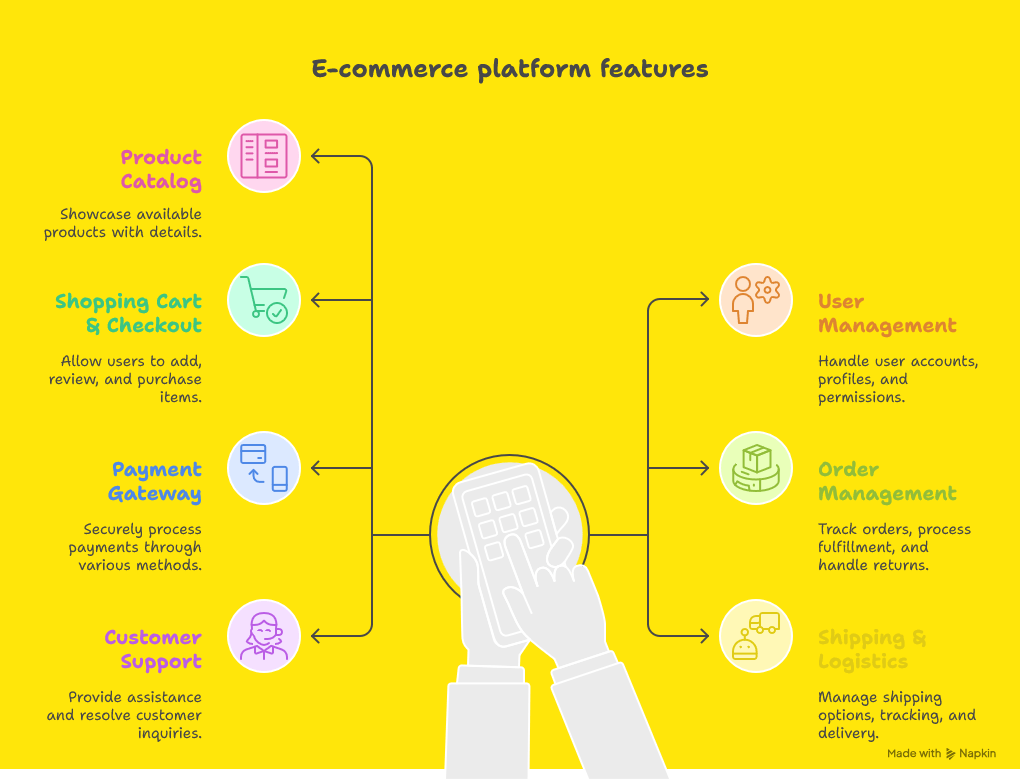
2. Product Catalog Service
Responsibilities:
- Maintain product master data: SKUs, descriptions, attributes, pricing tiers, media (images/videos).
- Support categorization, tagging, and hierarchical relationships (collections, bundles).
- Provide search and filtering capabilities via APIs.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Decoupled from inventory ensures product details can be updated independently.
- Versioning support allows staged roll‑out of new product attributes.
- Integrates with Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for fast media delivery.
Integration Points:
- Search & Discovery Service leverages catalog data to build indexes.
- Shopping Cart Service fetches product info for display and pricing.
- Promotions Service retrieves applicable items for discounts.
A robust Product Catalog Service under SOA empowers merchandising teams with agility to update offerings without impacting checkout workflows(AWS).
3. Inventory Management Service
Responsibilities:
- Track stock levels, reservations, allocations, and replenishments across warehouses, stores, and dropship suppliers.
- Handle concurrency, preventing overselling by employing locking or optimistic algorithms.
- Provide real-time availability data and notifications on low or out‑of‑stock thresholds.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Enables multi‑warehouse, multi‑region fulfillment with centralized control.
- Automates restocking workflows by integrating with supplier EDI/API.
- Exposes inventory levels to front-end channels to adjust customer expectations.
Integration Points:
- Order Management Service reserves and releases inventory upon order creation/cancellation.
- Shipping Service confirms availability for order picking and packing.
- Analytics Service monitors turnover rates and stock health.
With clear service boundaries, Inventory Management can scale based on transactional volume without hindering other business services(Medium).
4. Shopping Cart Service
Responsibilities:
- Maintain ephemeral or persistent shopping carts per customer or anonymous session.
- Support add/remove item operations, quantity updates, and guest checkouts.
- Calculate real-time subtotals, taxes, shipping estimates, and discounts.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Persisted carts allow shoppers to resume sessions on any device.
- Stateless APIs facilitate horizontal scaling behind load balancers.
- Integration with promotions and pricing engines renders accurate totals.
Integration Points:
- Pricing & Promotions Service applies active coupons, dynamic pricing, and loyalty rewards.
- Customer Management Service associates carts to authenticated users.
- Checkout Orchestration collects cart contents for final order submission.
A standalone Shopping Cart Service accelerates front‑end innovation by isolating cart lifecycle logic from backend order orchestration(Oracle).
5. Pricing & Promotions Service
Responsibilities:
- Manage price lists, discount rules, coupon campaigns, loyalty point redemptions, and dynamic pricing algorithms.
- Evaluate promotion eligibility and calculate price adjustments in real time.
- Provide audit trails and campaign performance metrics.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Enables complex B2B pricing models (volume discounts, contract pricing).
- Dynamic segmentation supports personalized offers based on customer attributes.
- Decoupled rules engine ensures rapid deployment of marketing promotions.
Integration Points:
- Shopping Cart Service invokes promotion evaluation before displaying totals.
- Order Management Service captures finalized prices for invoicing.
- Analytics Service tracks promotion redemption ROI.
By centralizing promotional logic, businesses can synchronize cross‑channel campaigns ‘always on’ and measure impact in near real time(AWS).
6. Checkout Orchestration Service
Responsibilities:
- Coordinate the end‑to‑end checkout workflow: cart validation, payment capture, inventory reservation, and order creation.
- Handle rollback scenarios (e.g., payment failure or inventory unavailability).
- Expose idempotent APIs to prevent duplicate orders.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Implements a saga pattern or transaction coordinator to maintain data consistency across services.
- Provides step‑by‑step progress tracking for front‑end user feedback.
- Ensures resilience with circuit breakers and retry mechanisms.
Integration Points:
- Payment Service for secure authorization and capture.
- Inventory Service for final reservation.
- Order Management Service to persist completed orders.
- Notification Service to send order confirmation communications.
This orchestration layer simplifies the complexities of distributed transactions in an e‑commerce environment(Medium).
7. Payment Service
Responsibilities:
- Integrate with external payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal, Adyen) and alternative methods (Apple Pay, Google Pay, BNPL).
- Handle tokenization, vaulting of payment instruments, and PCI DSS compliance.
- Support authorization, capture, refunds, voids, and dispute management.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Single abstraction layer for multiple gateway relationships.
- Risk management and fraud screening integration.
- Secure storage of payment tokens without exposing raw card data.
Integration Points:
- Checkout Orchestration Service for authorization and capture calls.
- Order Management Service to record payment status.
- Notification Service to alert customers about payment issues or confirmations.
Decoupling payment logic enables seamless addition of new payment providers and improves fault isolation in financial processes(Oracle).
8. Order Management Service
Responsibilities:
- Persist and manage order lifecycle states: received, processing, shipped, delivered, cancelled, returned.
- Expose order search, modification (address changes), and reorder APIs.
- Interface with warehouse management systems (WMS), shipping carriers, and third‑party logistics (3PL).
Key Features & Benefits:
- Central order hub supports omnichannel operations (online, in‑store pickup, returns).
- Workflow engine for manual or automated fulfillment rules.
- SLA tracking with automated escalations for delayed shipments.
Integration Points:
- Inventory Service for reservation and deallocation.
- Shipping Service to generate labels and tracking.
- Customer Management Service to display order history.
- Returns & Refunds Service to handle post‑delivery issues.
An independent Order Management Service ensures end‑to‑end visibility, fault tolerance, and business continuity during high‑traffic events(Port).
9. Shipping & Logistics Service
Responsibilities:
- Calculate shipping rates, delivery estimates, and label generation for multiple carriers (UPS, FedEx, DHL).
- Track shipments and update statuses through carrier webhooks.
- Coordinate multileg shipments, dropship, and cross‑border compliance (duties, taxes).
Key Features & Benefits:
- Real-time rate shopping ensures cost‑effective carrier selection.
- Automated batch label printing optimizes warehouse throughput.
- Customer‑facing tracking links improve transparency.
Integration Points:
- Order Management Service requests label creation and updates fulfillment status.
- Tax & Compliance Service for cross‑border orders.
- Notification Service to communicate shipment progress.
Shipping Service isolation allows the e‑commerce platform to support new fulfillment models and carriers without disrupting core order workflows(AWS).
10. Returns & Refunds Service
Responsibilities:
- Manage return merchandise authorizations (RMAs), exchanges, and replacement orders.
- Calculate refund amounts, restocking fees, and initiate payment reversals.
- Update inventory for returned items and trigger quality inspections.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Self‑service portals empower customers to start returns online.
- Automated correspondence reduces manual support overhead.
- Analytics on return reasons drives product quality improvements.
Integration Points:
- Order Management Service to flag orders as returned or exchanged.
- Inventory Service to restock returned items.
- Payment Service to process refunds.
- Notification Service to confirm return status with customers.
A dedicated Returns & Refunds Service improves operational efficiency and enhances customer trust by streamlining post‑purchase processes(Oracle).
11. Tax & Compliance Service
Responsibilities:
- Calculate sales tax, VAT, GST, and import duties based on tax jurisdiction rules.
- Handle tax exemptions for B2B customers and regulatory reporting.
- Keep tax tables up‑to‑date through integrations with external tax engines (Avalara, TaxJar).
Key Features & Benefits:
- Ensures accurate taxation, mitigating compliance risks.
- Simplifies expansion into new geographies with localized tax logic.
- Generates tax reports for accounting and audit purposes.
Integration Points:
- Checkout Orchestration Service and Order Management Service for tax calculation at order placement.
- Finance & Accounting Service to record tax liabilities.
- Analytics Service for tax revenue insights.
Centralizing tax logic in an SOA environment streamlines legal compliance and reduces the burden on development teams(Port).
12. Notification & Communication Service
Responsibilities:
- Send transactional and promotional emails, SMS messages, and push notifications.
- Manage templates, personalizations, localization, and scheduling.
- Track delivery, opens, clicks, and unsubscribes.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Unified messaging hub for consistent customer communications.
- Integration with third‑party email/SMS providers (SendGrid, Twilio).
- Automated triggers based on service events (order placed, shipped, abandoned cart).
Integration Points:
- Checkout Orchestration Service triggers order confirmations.
- Marketing Service dispatches newsletters and campaigns.
- Returns Service communicates RMA status updates.
By externalizing communication workflows, the Notification Service ensures reliable message delivery and simplifies compliance with CAN‑SPAM, GDPR, and TCPA regulations(AWS).
13. Marketing & Campaign Service
Responsibilities:
- Orchestrate email marketing, push campaigns, and retargeting ads based on customer behavior.
- Segment customers by demographics, purchase history, and browsing patterns.
- Manage A/B testing, drip sequences, and loyalty programs.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Increases customer lifetime value through personalized engagement.
- Integrates with customer data platform (CDP) for holistic profiles.
- Real‑time event ingestion from front-end or server events.
Integration Points:
- Customer Management Service for segmentation attributes.
- Analytics Service for campaign performance metrics.
- Notification Service for message delivery.
A stand‑alone Marketing Service allows rapid iteration of promotional strategies without impacting core order processes(Oracle).
14. Search & Discovery Service
Responsibilities:
- Index product data for full‑text search, faceted navigation, and recommendations.
- Support autocomplete suggestions, synonyms, and spelling corrections.
- Provide personalization by blending behavioral data and product attributes.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Improves conversion rates with fast, relevant search results.
- Offers merchandising controls for boosted or blacklisted SKUs.
- Scales horizontally to handle search spikes during peak shopping seasons.
Integration Points:
- Catalog Service supplies product metadata for indexing.
- Analytics Service logs search queries and click‑through rates.
- Front‑End Channels call search APIs for storefront rendering.
Decoupling search infrastructure from application servers avoids performance bottlenecks under heavy indexing or query loads(AWS).
15. Analytics & Reporting Service
Responsibilities:
- Collect events across all modules: page views, cart updates, purchases, returns, marketing interactions.
- Aggregate and analyze data to produce dashboards, KPIs, and predictive insights (e.g., churn risk).
- Support ad hoc queries, data exports, and integration with BI tools (Tableau, Looker).
Key Features & Benefits:
- Data lake or warehouse integration for historical analytics.
- Real-time streaming for immediate operational alerts (inventory stockouts, failed payments).
- Machine learning pipelines for recommendations and demand forecasting.
Integration Points:
- All Business Services emit standardized events.
- Marketing Service consumes audience segments for campaigns.
- Finance Service uses revenue reports for financial planning.
An independent Analytics Service ensures business teams can innovate with data models without jeopardizing transactional performance(AWS).
16. Finance & Accounting Service
Responsibilities:
- Record all financial transactions: sales, refunds, shipping fees, taxes, and commission reconciliations.
- Generate invoices, credit memos, and financial statements.
- Integrate with ERP systems (SAP, Oracle E‑Business Suite) for general ledger postings and reconciliation.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Ensures financial integrity and auditability.
- Automates billing and subscription renewals for recurring revenue models.
- Provides multi‑currency support and FX rate management.
Integration Points:
- Order Management Service for sales orders and invoices.
- Returns Service for refund journal entries.
- Tax Service for tax liability reporting.
- Payment Service for reconciliation of captures and refunds.
Separating accounting logic prevents leakage of sensitive financial processes into public‑facing modules and facilitates compliance with GAAP/IFRS standards(Port).
17. User Experience & Presentation Services
Responsibilities:
- Host front‑end applications: web storefront, mobile apps, in‑store kiosks, and PWA clients.
- Aggregate data from backend services through API gateway or GraphQL layer.
- Implement caching, edge rendering, and CDN distribution for performance.
Key Features & Benefits:
- Enables A/B tests and iterative UI updates without redeploying backend services.
- Provides consistent user interfaces across channels with shared component libraries.
- Improves SEO and accessibility through server‑side rendering or pre‑rendered content.
Integration Points:
- API Gateway routes requests to underlying services.
- Search Service, Cart Service, Product Service for data retrieval.
- Authentication Service for access control to protected pages.
A dedicated presentation layer decouples UI innovation from business logic, accelerates time‑to‑market, and ensures cohesive brand experiences(AWS).
Conclusion
Adopting a Service-Oriented Architecture empowers e‑commerce companies to build modular, scalable, and resilient platforms. By decomposing the system into focused services—Customer Management, Product Catalog, Inventory, Cart, Pricing, Checkout, Payment, Order Management, Shipping, Returns, Tax, Notifications, Marketing, Search, Analytics, Finance, and Presentation—businesses can:
- Accelerate feature development through independent service teams.
- Scale mission‑critical components based on demand surges.
- Integrate best‑of‑breed third‑party solutions without monolithic constraints.
- Improve fault isolation and maintain high availability.
As digital commerce continues to evolve, a robust SOA foundation ensures that organizations can swiftly adapt to emerging trends, regulations, and customer expectations. By thoughtfully defining clear service boundaries, embracing API‑first design, and implementing reliable inter-service communication patterns, e‑commerce platforms will remain agile, performant, and resilient for years to come.
Quantum-Ready E-Commerce: Practicing Q-SCALE Phase-Wise
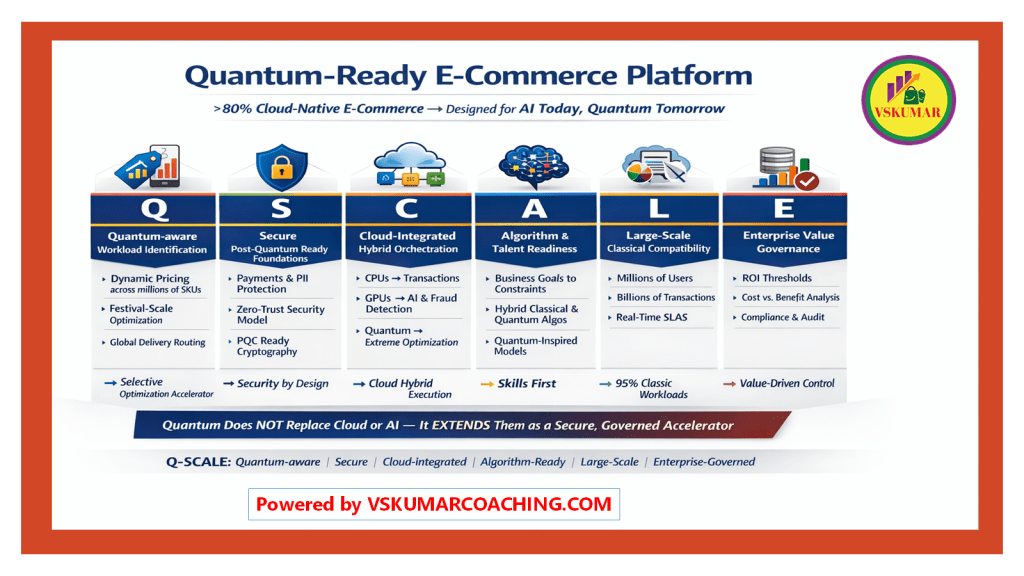
Look forward for next solutions on how to migrate these modules into AI agents based systems.
