Solution Specification – AI-Powered Data Analysis Agent
Overview
The AI-driven Data Analysis Agent is designed to process large datasets, identify trends, and generate insights for strategic decision-making. The system automates data cleaning, visualization, and predictive modeling, enhancing efficiency and reducing manual effort.
Scenario 1: AI-Powered Customer Analytics for E-Commerce
1. Problem Statement
E-commerce businesses often struggle with understanding customer preferences and predicting sales trends. Manual data analysis takes time and may result in inaccurate insights.
2. Proposed AI Agent Solution
An AI-driven Customer Behavior Analysis Agent that:
- Aggregates customer purchase history, browsing patterns, and engagement data.
- Performs sentiment analysis on product reviews to assess satisfaction levels.
- Uses machine learning to segment customers based on shopping habits.
- Generates predictive sales insights to anticipate demand fluctuations.
3. Technical Specification
- Data Sources: Website traffic logs, CRM systems, payment transaction databases.
- Processing Engine: Python-based frameworks (Pandas, NumPy) and Azure AI tools.
- ML Models: Customer clustering (K-Means), predictive sales forecasting (LSTM neural networks).
- Visualization Tools: Power BI for dynamic dashboards and trend analysis.
4. Live Scenario Implementation
Retail Company X integrates the AI agent into its e-commerce analytics system:
- The agent analyzes past purchase trends and identifies peak shopping seasons.
- Sentiment analysis reveals which products need improvement based on customer feedback.
- Predictive models suggest personalized discount offers for high-value customers.
- The system provides real-time insights to optimize inventory and prevent stock shortages.
5. Benefits
✔ Improves customer experience with personalized recommendations.
✔ Reduces inventory waste by predicting demand effectively.
✔ Automates data processing, saving manpower and time.
Scenario 2: AI-Based Financial Fraud Detection for Banking
1. Problem Statement
Banks face difficulties in detecting fraudulent transactions due to high volumes of financial data. Traditional fraud detection methods rely on predefined rules, missing evolving fraud patterns.
2. Proposed AI Agent Solution
An AI-powered Fraud Detection & Risk Assessment Agent that:
- Analyzes real-time transaction data for anomalies.
- Flags suspicious activities using behavioral analysis and fraud pattern detection.
- Learns dynamically from new fraud cases to enhance detection accuracy.
- Generates risk alerts and automated compliance reports.
3. Technical Specification
- Data Sources: Transaction logs, banking APIs, credit card purchase records.
- Processing Engine: Big data processing with Apache Spark and SQL-based analysis.
- ML Models: Anomaly detection (Isolation Forest), fraud classification (Random Forest).
- Integration: Connects to banking security systems via REST APIs.
4. Live Scenario Implementation
Bank Y deploys the AI fraud detection system across its financial transactions:
- The agent detects unusual spending patterns and flags potential fraud.
- It analyzes location-based transactions to identify suspicious activity (e.g., rapid withdrawals across different cities).
- AI alerts compliance teams automatically, improving response time for fraudulent cases.
- The bank reduces fraud losses by adapting models dynamically based on new threats.
5. Benefits
✔ Improves fraud detection accuracy with AI-driven insights.
✔ Enhances security by identifying evolving fraud techniques.
✔ Reduces financial losses and increases customer trust.
Conclusion
These two AI agents—Customer Analytics for E-Commerce and Fraud Detection for Banking—demonstrate how AI-powered Data Analysis Agents can optimize decision-making, automate data insights, and enhance risk management.
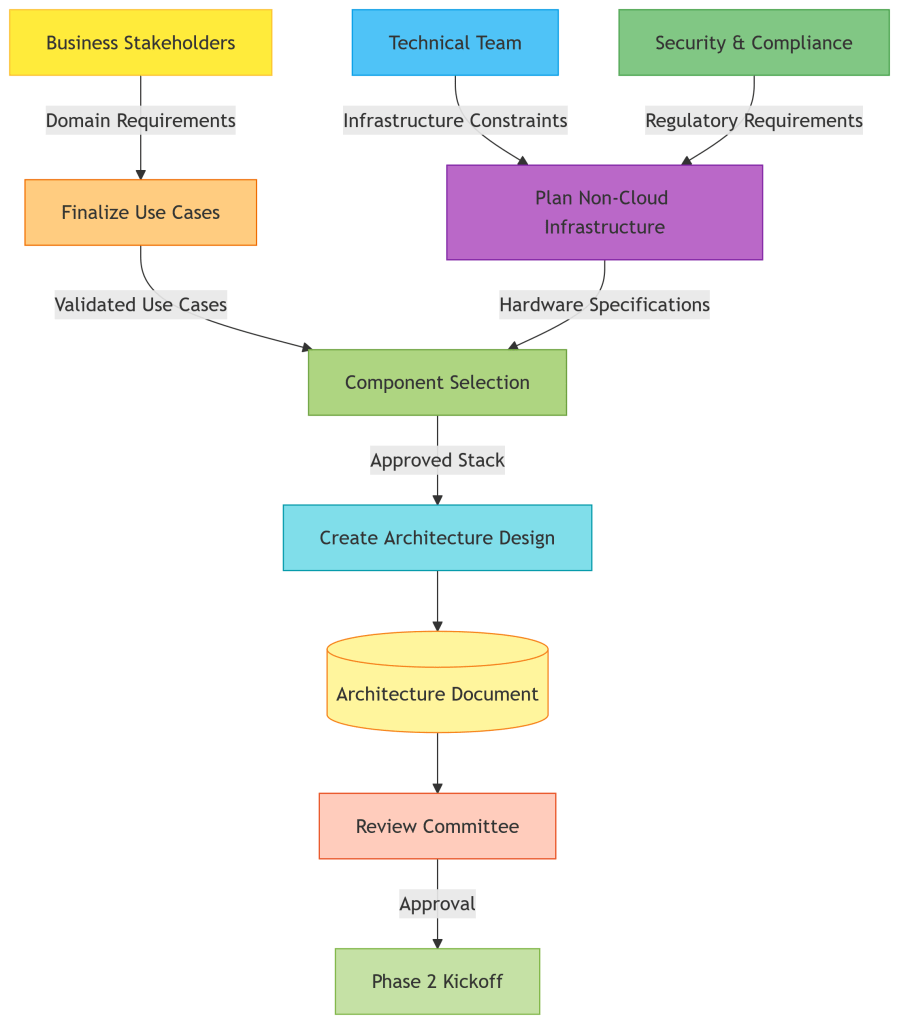
To complement the AI-powered Data Analysis Agent, here’s a sample Database Specification for storing and managing data efficiently.
The Blog Discussion video:
Learn How we built the Project planning/phases with Deep Seek Solution:
Deep Seek solution for Phases planning:
Sample Database Specifications for AI-Powered Data Analysis Agent
1. Database Type
- Relational Database (SQL-based): Suitable for structured data (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQL Server).
- NoSQL Database (Document-based): For flexible, unstructured data (e.g., MongoDB, Elasticsearch).
- Hybrid Approach: Combining structured and unstructured data storage.
2. Sample Database Schema
Below is a simplified schema for both scenarios:
Scenario 1: Customer Analytics for E-Commerce
Database Name: customer_analytics_db
| Table Name | Fields | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
customers | customer_id (PK), name, email, location, gender, age | INT, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, INT | Stores user details |
transactions | transaction_id (PK), customer_id (FK), date, total_amount, payment_method | INT, INT, DATE, DECIMAL, VARCHAR | Stores purchase details |
products | product_id (PK), name, category, price, stock_available | INT, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, DECIMAL, INT | Stores product details |
customer_behavior | customer_id (FK), browsing_time, pages_visited, click_through_rate | INT, TIME, INT, FLOAT | Stores browsing behavior details |
sentiment_analysis | review_id (PK), customer_id (FK), product_id (FK), review_text, sentiment_score | INT, INT, INT, TEXT, FLOAT | Stores sentiment analysis results |
Scenario 2: Fraud Detection for Banking
Database Name: fraud_detection_db
| Table Name | Fields | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
transactions | transaction_id (PK), customer_id (FK), amount, location, transaction_type, timestamp | INT, INT, DECIMAL, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, TIMESTAMP | Stores transaction details |
fraud_cases | case_id (PK), transaction_id (FK), fraud_flag, risk_score, remarks | INT, INT, BOOLEAN, FLOAT, TEXT | Stores fraud alerts and analysis |
customer_accounts | customer_id (PK), account_number, account_type, balance, status | INT, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, DECIMAL, VARCHAR | Stores customer banking details |
device_activity | device_id (PK), customer_id (FK), ip_address, device_type, last_seen | INT, INT, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, TIMESTAMP | Stores device & login activity |
alerts_log | alert_id (PK), customer_id (FK), alert_type, severity, timestamp | INT, INT, VARCHAR, VARCHAR, TIMESTAMP | Logs security warnings & notifications |
3. Key Features
✔ Indexing & Optimization – Ensures quick retrieval of patterns & insights.
✔ Real-Time Data Processing – Supports immediate fraud detection & customer analytics.
✔ Secure Access & Compliance – Adheres to financial & GDPR regulations.
✔ Scalability – Can handle growing data volumes efficiently.
Here are some AI Design-related Interview Questions that can be used for a blog post focusing on AI Agent Development and Data Analysis Systems:
AI Agent Design – Interview Questions and Answers for Interviews
Certainly! Here are the answers to the 20 AI Design-related interview questions, covering aspects of AI agents, data analysis, system architecture, deployment, and integration.
AI Agent Design – Interview Questions and Answers
1. General AI Design Questions
- How do you approach designing AI agents that balance efficiency and adaptability?
AI agents must be designed with modular architectures that allow customization and scalability. Using techniques like transfer learning and reinforcement learning, agents adapt to new environments without requiring extensive retraining. - What are the key components required to build a scalable AI architecture?
A scalable AI system needs:- Efficient data pipelines to handle large datasets
- Cloud-based computing for scalability
- Automated model retraining to stay updated
- API-driven communication for integration with other systems
- How do you ensure AI models avoid biases when analyzing large datasets?
- Implement fairness-aware machine learning techniques
- Use diverse and representative training datasets
- Regularly audit AI decisions for bias detection
- Fine-tune models with ethical AI principles
- What role does data preprocessing play in AI system performance?
Data preprocessing ensures clean, structured input for AI models, reducing noise and improving accuracy. Key steps include data normalization, outlier removal, and handling missing values. - How do you integrate ethical considerations into AI-driven decision-making systems?
- Establish transparent AI policies
- Implement explainability models (e.g., SHAP or LIME)
- Ensure human oversight in critical decisions
- Follow legal frameworks like GDPR and AI governance laws
2. Data Analysis Agent-Specific Questions
- How can an AI-powered data analysis agent enhance business intelligence?
AI agents automate data processing, identifying trends, anomalies, and predictive insights to assist decision-makers in refining strategies. - What challenges arise when training AI models for real-time data processing?
- Latency issues from continuous data streams
- Handling incomplete or noisy real-time data
- Balancing speed vs. accuracy in predictions
- How do AI agents differentiate between valuable insights and noise in big data analytics?
- Feature selection algorithms help filter relevant data
- Anomaly detection eliminates misleading trends
- Statistical modeling refines data significance
- What techniques can be used to improve the accuracy of AI-generated predictions?
- Hyperparameter tuning to optimize models
- Ensemble learning combining multiple models
- Cross-validation for robust model evaluation
- How do AI systems handle unstructured data, such as text and images, in analytics?
AI models utilize:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for text analysis
- Computer Vision for image processing
- Deep learning-based embeddings to structure raw data
3. System Architecture & Implementation
- What database structure is best suited for AI-driven analytics systems?
Hybrid models combining SQL and NoSQL databases offer the best balance for structured and unstructured data storage. - How do AI agents interact with cloud-based services for large-scale processing?
- RESTful APIs connect agents to cloud services
- Serverless computing (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) enables scalable execution
- Data warehouses (e.g., Google BigQuery, Snowflake) facilitate large-scale analytics
- What factors determine the choice between SQL and NoSQL databases for AI applications?
- SQL for structured, relational data analysis
- NoSQL (MongoDB, Elasticsearch) for flexible, semi-structured data
- How do AI agents optimize query performance when handling large datasets?
- Indexing and caching techniques speed up queries
- Distributed computing frameworks (Hadoop, Spark) enhance data processing
- Parallel execution boosts efficiency
- What security measures must be considered when designing AI agents for financial fraud detection?
- End-to-end encryption for secure transactions
- Anomaly detection models for fraud prevention
- Regulatory compliance (PCI DSS, GDPR, SOC 2)
4. AI Deployment & Integration
- How do AI models integrate with existing business workflows?
AI models connect via:
- APIs for seamless business software integration
- Microservices architecture ensuring modular design
- Automation tools (RPA, AI-driven alerts)
- What are common challenges faced when deploying AI-powered automation solutions?
- Resistance to change from employees
- Integration complexity with legacy systems
- High computational costs for model inference
- How do AI agents update and evolve based on new data and industry trends?
- Continuous learning models improve predictions over time
- Retraining pipelines ensure adaptation
- Active learning refines AI based on feedback
- What strategies ensure AI-driven analytics provide actionable insights instead of just raw data?
- Context-aware insights instead of raw metrics
- Data storytelling visualization for easy interpretation
- Customizable dashboards for executive decision-making
- How do AI-powered agents improve cross-functional decision-making within organizations?
- Consolidating data from multiple departments
- Providing unified analytics dashboards
- Generating insights tailored to business objectives
Conclusion
These AI design, analytics, and deployment interview questions and answers provide valuable insights into developing scalable, efficient, and adaptable AI agents. They cover technical implementation, business impact, and best practices in AI system design.
This set of questions can stimulate discussions and insights into AI design, system architecture, deployment, and analytics for interviews.
During our Job Coaching you will be designing/developing this kind of products and making you for doing demos for your profile scale up. DM me for your scale up program.

Solution demo by Rahul Patil [ML Engineer]-21st June 2025:
Phase1 Technical setup demo by Rahul Patil [ML Engineer] on 29th June 2025:
Ravi Kumar [NONIT] Created a Project plan document for 7 phases of this project, you can see his demo.
Data Analysis Agent-Project Plan document discussion by Ravi Kumar [NONIT]- 2-06-2025
Solution demo by Ravi Kumar[NONIT] on 23rd June 2025:
Phase1 Technical setup demo by Ravi [NONIT] on 10th July 2025:
Note:
Keep visiting this blog for further phases solutions.
What we do and how we scale up the IT Professionals skills into AI Role?
At vskumarcoaching.com, we shape AI Consultants through hands-on, real-world project experience. These professionals present their work as live POCs to showcase their execution skills and strategic thinking.
As a result, their resumes gain high visibility among recruiters, making them highly sought-after in today’s competitive job market. Our mission is to empower professionals to level up and secure consistent, long-term careers in IT. This is where the large IT services cos build the Resources [under Center of Excellence] with latest skills to showcase to their Client on their competencies.
The planning phases document is explained by Ravi. [he is a NON IT Professional: https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravikumar-kangne-364207223/