Thriving in the Age of AI: The Skills That Matter
(Intro + human skills sections remain the same as before — I’ll keep them intact and focus on expanding the roadmap with “in‑house build” alternates.)
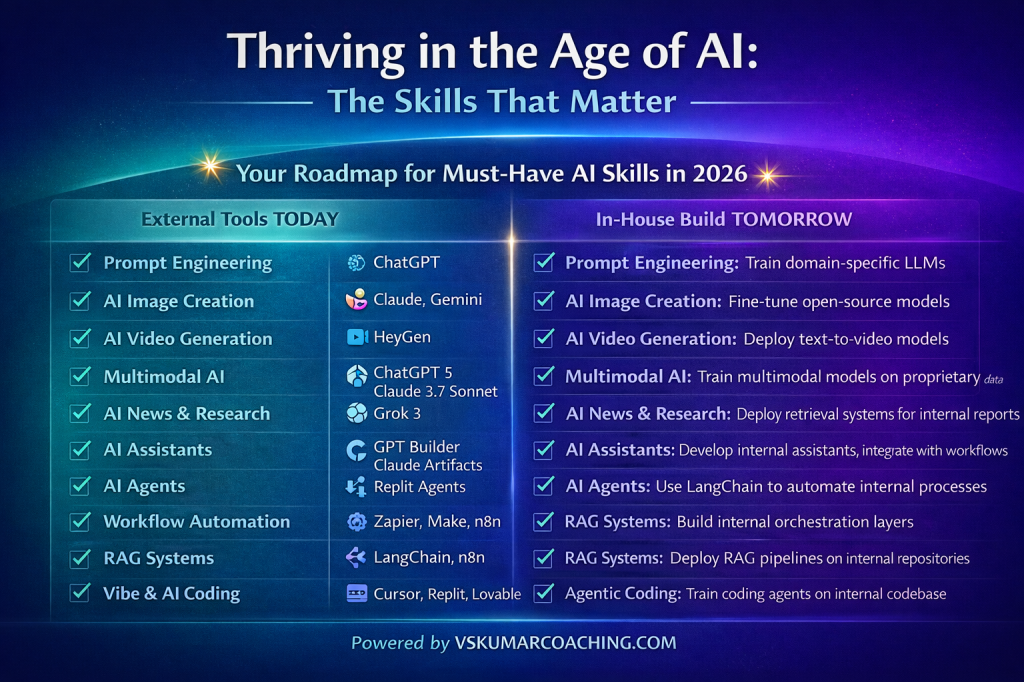
💥 Your Roadmap for Must-Have AI Skills in 2026
1. Prompt Engineering
Intro: At the heart of AI interaction lies the ability to communicate clearly. Prompt engineering is the skill of crafting precise instructions that guide AI toward useful, reliable outputs.
- Write precise, context-clear instructions for reliable results
- Break work into steps and guide AI with clean inputs
- Tools: ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini
In‑House Build:
- Train domain-specific LLMs with curated prompts and responses from your own workflows.
- Build a prompt library inside a knowledge base for reusable, standardized instructions.
- Develop internal “prompt QA” systems to test reliability before deployment.
2. AI Image Creation
Intro: Visual storytelling is now accessible to everyone. AI image creation allows professionals to turn abstract ideas into compelling visuals in seconds.
- Transform ideas into visuals for content, design, and storytelling
- Rapid prototyping and concept testing
- Tools: Midjourney, Ideogram, Nana Banana
In‑House Build:
- Fine-tune open-source diffusion models (e.g., Stable Diffusion) on brand assets.
- Host internal image generation pipelines with compliance filters.
- Create a style guide model that enforces brand colors, fonts, and recruiter-neutral visuals.
3. AI Video Generation
Intro: Video has become the dominant medium for communication, and AI makes it effortless. With no cameras or editing teams, you can produce professional content in minutes.
- Produce videos without cameras or editing teams
- Speed up training, updates, and content creation
- Tools: HeyGen, Runway, Opus
In‑House Build:
- Deploy text-to-video models on secure servers for training content.
- Integrate avatars or synthetic presenters aligned with company branding.
- Build modular templates for onboarding, compliance, or product demos.
4. Multimodal AI
Intro: The future of AI is multimodal—systems that can process text, images, audio, and video together. This unlocks richer insights and more integrated workflows.
- AI that processes text, images, video, and audio together
- Unified models for research, planning, and creation
- Tools: ChatGPT 5, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Grok 3
In‑House Build:
- Train multimodal models on proprietary datasets (documents + visuals + audio).
- Build pipelines that unify customer support transcripts, product images, and manuals.
- Create dashboards where multimodal AI powers research and planning in one interface.
5. AI News and Research
Intro: Staying informed is critical, but information overload is real. AI research tools help professionals cut through the noise and surface what matters.
- Quick answers, deep insights, and trend scanning
- Summarize long documents and reports efficiently
- Tools: Perplexity, Claude, ChatGPT Search
In‑House Build:
- Deploy retrieval systems connected to internal reports, compliance docs, and market feeds.
- Build summarization engines tuned to your industry language.
- Create “trend dashboards” that auto-scan internal + external sources for executives.
6. AI Assistants
Intro: Personalized AI assistants are becoming everyday productivity partners. They organize work, repeat tasks, and adapt to your style.
- Build personalized AI helpers that organize work and repeat tasks
- Style-aligned assistants for productivity
- Tools: GPT Builder, Claude Artifacts, Replit Agents
In‑House Build:
- Develop internal assistants trained on company workflows (HR, finance, project management).
- Integrate assistants with calendars, CRMs, and ticketing systems.
- Build modular “assistant APIs” that employees can customize for their roles.
7. AI Agents
Intro: Beyond assistants, AI agents can autonomously handle multistep workflows. They execute tasks in the background, freeing you to focus on strategy.
- Automate multistep workflows end-to-end
- Run background tasks while focusing on decisions
- Tools: LangChain, CrewAI, AutoGen
In‑House Build:
- Use frameworks like LangChain to orchestrate internal processes (approvals, reporting).
- Train agents to handle compliance-heavy workflows securely.
- Build monitoring dashboards to track agent performance and decision logs.
8. Workflow Automation
Intro: Efficiency is about removing friction. Workflow automation connects tools so repetitive tasks happen seamlessly without human intervention.
- Connect tools for seamless task handoffs
- Automate repetitive updates and communications
- Tools: Zapier, Make, n8n
In‑House Build:
- Build internal orchestration layers that connect ERP, CRM, and HR systems.
- Use event-driven architecture for auto-triggered workflows.
- Create compliance-safe automation pipelines for sensitive data.
9. RAG Systems (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
Intro: AI is most powerful when connected to your own data. RAG systems ensure answers are accurate, context-specific, and business-ready.
- Link AI to your own data for accurate, context-specific answers
- Convert PDFs and documents into instant responses
- Tools: LangChain, LlamaIndex, Vectara
In‑House Build:
- Deploy RAG pipelines on internal document repositories.
- Build embeddings tuned to your company’s terminology.
- Create secure query interfaces for employees to access knowledge instantly.
10. Vibe and AI Coding
Intro: Not every project needs heavy coding. AI coding tools let you prototype quickly, test ideas, and iterate without deep technical expertise.
- Rapid prototyping with minimal coding
- Build small tools quickly for testing and iteration
- Tools: Cursor, Replit, Lovable
In‑House Build:
- Set up internal sandboxes for rapid prototyping with AI coding copilots.
- Build “innovation labs” where employees test ideas safely.
- Integrate low-code AI platforms with company APIs for quick experiments.
11. Agentic Coding
Intro: For larger projects, agentic coding allows you to delegate entire coding tasks to AI agents that plan and execute autonomously.
- Delegate full coding tasks to AI agents
- Describe outcomes and let AI plan/execute steps
- Tools: O1 Codex, Claude Code, Replit
In‑House Build:
- Train coding agents on your internal codebase for context-aware development.
- Build governance layers to review agent-generated code before deployment.
- Use containerized environments for safe agent execution.
12. AI-Assisted Development
Intro: Software development is being transformed by AI copilots. They accelerate debugging, rewriting, and feature building—making development faster and more reliable.
- Accelerate software building and debugging
- Fix errors, rewrite code, and update features in minutes
- Tools: Cursor, Gemini Code Assist, GitHub Copilot
In‑House Build:
- Deploy AI copilots trained on your proprietary code repositories.
- Integrate copilots into IDEs used across the company.
- Build automated QA pipelines where AI suggests fixes and improvements.
Moving Forward
The professionals who will stand out are not those who try to outpace AI, but those who learn to work with it. Instead of drowning in the pressure to “learn it all,” they focus on building a toolkit of durable human skills—paired with practical AI capabilities that amplify their impact.
AI may be advancing daily. But with the right blend of judgment, creativity, adaptability, and these twelve must-have skills—whether through external tools or in-house builds—so can you.