🔷 10 MCP Questions — Addressed Directly to CXOs
1. How do we scale AI across the enterprise without increasing regulatory, compliance, and reputational risk?
(MCP introduces governed, auditable AI contexts instead of ad-hoc prompts.)
2. How can we trust AI decisions when data, documents, and tools are spread across teams and systems?
(MCP unifies enterprise context with policy-bound access.)
3. What governance framework ensures AI outputs are explainable to auditors, regulators, and boards?
(MCP enforces Context Lineage (CL) and Policy-Based Reasoning (PBR).)
4. How do we prevent AI hallucinations from becoming business or legal liabilities?
(MCP restricts AI reasoning to approved, verified enterprise context.)
5. Can AI be enterprise-grade without slowing innovation and time-to-market?
(MCP standardizes context exchange—speed with control.)
6. How do we move AI from isolated pilots to organization-wide adoption safely?
(MCP acts as the integration layer between models, data, and governance.)
7. What does “AI-ready governance” look like before regulators define it for us?
(MCP becomes a proactive control mechanism.)
8. How do we ensure AI decisions align with company policies, ethics, and risk appetite?
(MCP embeds policy enforcement directly into AI context.)
9. What architectural foundation avoids future AI rework and vendor lock-in?
(MCP provides a model-agnostic, standardized protocol.)
10 How do we demonstrate measurable ROI from AI while maintaining trust and accountability?
(MCP enables scalable, auditable, and repeatable AI deployment.)
“This blog explains why MCP is emerging as the missing governance layer for enterprise AI — and how CXOs can adopt it before risk forces the decision.”
🚀 Model Context Protocol (MCP – Model Context Protocol): Turning Enterprise AI into Governed Business Systems
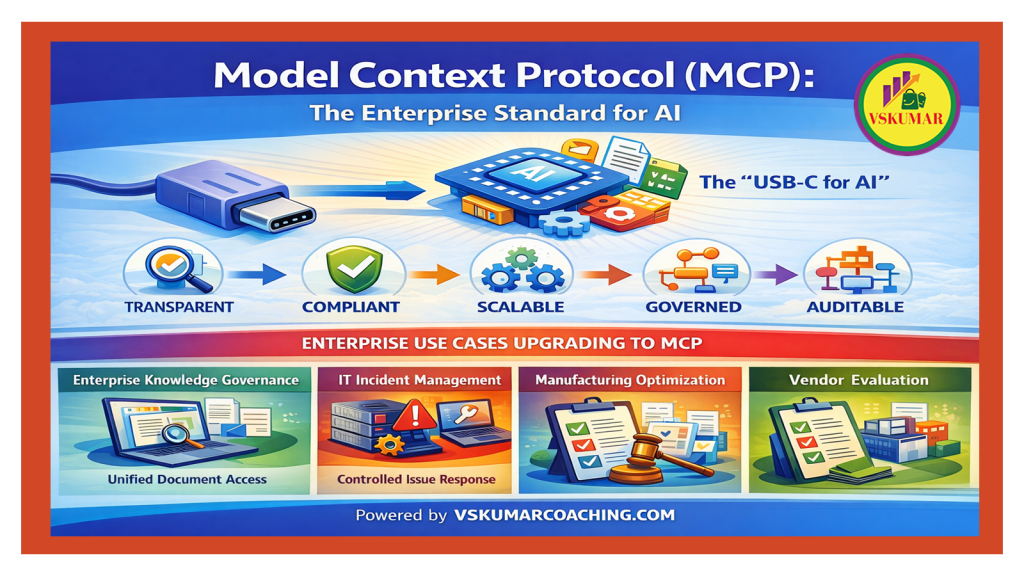
🧠 What Is MCP (Model Context Protocol)?
The Model Context Protocol (MCP – Model Context Protocol) is an open standard that defines how Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems securely and transparently interact with enterprise tools, data sources, and workflows.
Instead of embedding business logic inside hidden prompts, MCP externalizes context, actions, and decisions as explicitly defined components.
In simple terms, MCP acts as a control layer for enterprise AI, ensuring models behave like governed systems—not unpredictable assistants.
🌟 Why MCP (Model Context Protocol) Is Becoming an Enterprise Standard
As AI (Artificial Intelligence) moves from experimentation into production systems, organizations face serious challenges around explainability, governance, and compliance.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) solves these challenges by enforcing structure, traceability, and operational discipline across AI-driven workflows.
✅ Key Benefits of MCP (Model Context Protocol)
- Structured AI Execution (Artificial Intelligence Execution)
AI systems operate through predefined workflows rather than improvising logic. - End-to-End Traceability
Every decision can be traced back to specific tools, data sources, and prompts. - Reusable Enterprise Modules
AI workflows become reusable building blocks instead of one-off scripts. - Reduced Operational Risk
MCP constrains AI actions to approved enterprise boundaries. - Model and Vendor Independence
Business logic is decoupled from specific Large Language Models (LLMs – Large Language Models).
📌 Enterprise Use Cases Driving MCP (Model Context Protocol) Adoption
🧩 Use Case 1: Enterprise Knowledge Governance (EKG – Enterprise Knowledge Governance)
Business Context
Large enterprises manage thousands of internal documents such as policies, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs – Standard Operating Procedures), and architectural guidelines across multiple platforms.
Problem Before MCP (Model Context Protocol)
AI assistants retrieved information inconsistently, sometimes mixing outdated documents with current ones, with no visibility into source selection.
MCP Upgrade Decision
The organization implemented MCP to expose document repositories as version-controlled resources, along with governed search and summarization tools.
Justification
MCP ensured that AI responses were generated only from approved and current knowledge sources, with a full trace of document usage.
Outcome
Employees received consistent, policy-aligned answers with audit-ready transparency.
🧩 Use Case 2: IT Incident Diagnosis & Resolution (ITSM – Information Technology Service Management)
Business Context
IT teams rely on logs, alerts, monitoring dashboards, and runbooks to manage production incidents.
Problem Before MCP (Model Context Protocol)
AI tools analyzed logs independently and suggested fixes without understanding system dependencies or escalation rules.
MCP Upgrade Decision
Incident response workflows were rebuilt using MCP to expose log streams, diagnostic tools, dependency maps, and resolution runbooks as a single governed process.
Justification
MCP allowed IT leaders to inspect how AI recommendations were produced and ensured alignment with approved ITSM (Information Technology Service Management) practices.
Outcome
Incident resolution became faster, predictable, and fully auditable.
🧩 Use Case 3: Manufacturing Process Optimization (MPO – Manufacturing Process Optimization)
Business Context
Manufacturing plants collect sensor data, quality metrics, and production statistics from Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT – Industrial Internet of Things) systems.
Problem Before MCP (Model Context Protocol)
AI-driven insights varied across plants, creating inconsistencies in optimization recommendations.
MCP Upgrade Decision
MCP was used to expose sensor feeds, analytics engines, and optimization models with standardized evaluation prompts.
Justification
This ensured that all plants followed the same decision logic when improving efficiency or addressing defects.
Outcome
Operational improvements became consistent, measurable, and defensible.
🧩 Use Case 4: Corporate Policy Compliance Management (CPCM – Corporate Policy Compliance Management)
Business Context
Enterprises must continuously validate internal operations against regulatory and corporate policies.
Problem Before MCP (Model Context Protocol)
Compliance checks were manual, inconsistent, and difficult to explain during audits.
MCP Upgrade Decision
Compliance workflows were implemented through MCP by exposing policy rules, evidence sources, and validation tools.
Justification
MCP produced machine-verifiable compliance decisions with a transparent reasoning trail.
Outcome
Audit preparation time was reduced and compliance confidence increased.
🧩 Use Case 5: Strategic Vendor Evaluation (SVE – Strategic Vendor Evaluation)
Business Context
Procurement teams assess vendors using performance metrics, risk indicators, and contractual obligations.
Problem Before MCP (Model Context Protocol)
AI-generated vendor recommendations lacked transparency and varied across teams.
MCP Upgrade Decision
Vendor evaluation logic was rebuilt on MCP using explicit scoring models, data connectors, and decision prompts.
Justification
MCP enabled objective, repeatable vendor assessments aligned with enterprise governance.
Outcome
Vendor decisions became consistent, data-driven, and leadership-approved.

✨ Closing Perspective
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) does not make AI smarter—it makes AI trustworthy.
By converting AI behavior into structured, inspectable workflows, MCP allows enterprises to scale Artificial Intelligence (AI) responsibly across critical systems.
For organizations focused on governance, auditability, and long-term AI adoption, MCP is no longer optional—it is foundational.