Quantum-Ready E-Commerce: Practicing Q-SCALE Phase-Wise
As more than 80% of enterprise e-commerce systems operate on cloud infrastructure, organizations have an unprecedented opportunity to prepare for quantum computing adoption in a structured, value-driven way. Using the Q-SCALE framework—Quantum-aware, Secure, Cloud-integrated, Algorithm-ready, Large-scale, Enterprise-governed—we can break this journey into practical phases, each with actionable steps and real-world examples.

- 🧭 Demystifies quantum computing by explaining it in simple, business-friendly e-commerce scenarios
- 🛒 Connects quantum ideas to real e-commerce problems like pricing, delivery, inventory, and promotions
- 🧩 Introduces Q-SCALE clearly (Quantum-aware, Secure, Cloud-integrated, Algorithm-ready, Large-scale, Enterprise-governed)
- ☁️ Shows how quantum fits into today’s cloud systems, not as a replacement but as an accelerator
- 👥 Guides both leaders and professionals—from CXOs planning strategy to engineers exploring quantum careers
- 📈 Keeps business value first, ensuring stability, security, ROI, and governance at every step
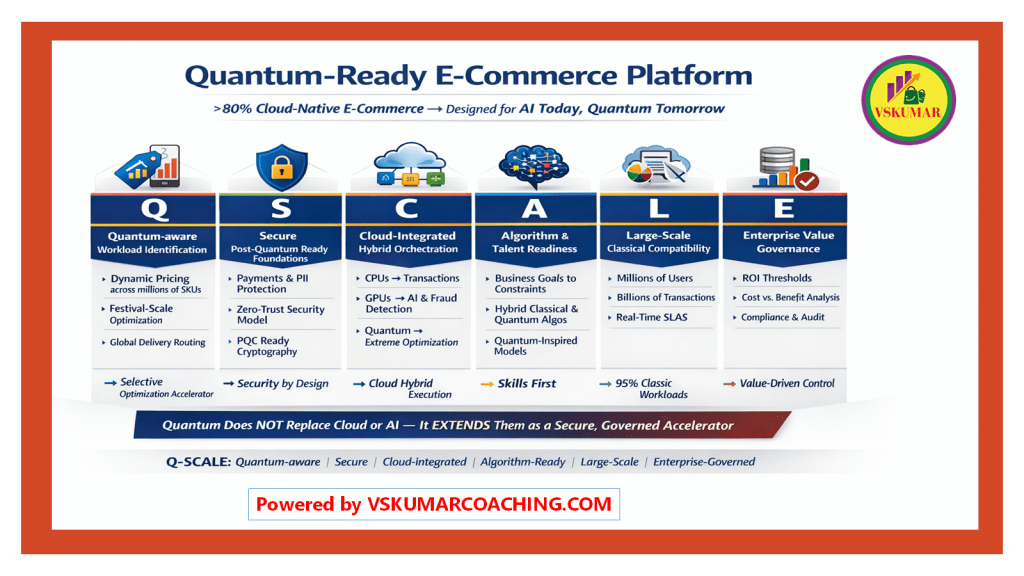
Phase 1: Quantum-aware Workload Identification (Q)
Goal: Identify high-complexity e-commerce scenarios where quantum computing could add significant value.
How to Practice
- Map all e-commerce operations and classify workloads by complexity and scale.
- Identify optimization-heavy operations that cannot be efficiently solved by classical methods alone.
Examples
- Dynamic Pricing Across Millions of SKUs (Stock Keeping Units): Using AI-driven pricing, highlight peak-sale scenarios where combinatorial pricing decisions explode in scale.
- Global Delivery Route Optimization: Simulate delivery routing for peak festival days to identify extreme-scale scenarios suitable for quantum-inspired solutions.
Outcome: Enterprises understand where quantum computing can act as a selective accelerator without disrupting day-to-day operations.
Phase 2: Secure, Post-Quantum-Ready Foundations (S)
Goal: Build security frameworks that anticipate the demands of quantum computing.
How to Practice
- Establish zero-trust architectures for sensitive e-commerce data like payments and customer information.
- Build crypto-agile frameworks capable of integrating Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) once quantum computing becomes mainstream.
Examples
- Payment & PII Protection: Encrypt sensitive data today using current standards, while ensuring the framework is PQC-ready for future migration.
- Fraud Detection Systems: Design AI-driven fraud detection pipelines that can accommodate quantum-enhanced anomaly detection without redesigning the core system.
Outcome: Security becomes a foundational enabler, not a post-implementation patch, making the platform quantum-ready from day one.
Phase 3: Cloud-Integrated Hybrid Orchestration (C)
Goal: Seamlessly integrate quantum computing as an extension of existing cloud infrastructure.
How to Practice
- Build orchestration layers to dynamically route workloads across CPUs, GPUs, and future quantum resources.
- Ensure all microservices and APIs are quantum-compatible by design, without rewriting existing business logic.
Examples
- AI Recommendation Engines: Run AI models on GPUs and reserve quantum computation for extreme personalization optimization during peak traffic.
- Inventory Optimization: Classical cloud computes normal inventory predictions while quantum simulation handles multi-warehouse allocation in high-demand scenarios.
Outcome: Quantum resources are plugged in as cloud accelerators, preserving current operations while extending computational capabilities.
Phase 4: Algorithm & Talent Readiness (A)
Goal: Develop problem-solving frameworks and skills to leverage quantum-inspired solutions.
How to Practice
- Train teams in hybrid classical-quantum algorithms and quantum-inspired heuristics.
- Reformulate business challenges into mathematical models that can scale to quantum computation when needed.
Examples
- Promotion Optimization: Use hybrid algorithms to balance promotional campaigns with inventory and pricing constraints.
- Checkout Conversion Optimization: Train teams to model customer behavior patterns and simulate extreme-scale scenarios with quantum-inspired algorithms.
Outcome: Talent and algorithms are ready for quantum adoption, independent of hardware availability.
Phase 5: Large-Scale Classical Compatibility (L)
Goal: Ensure classical systems remain stable and performant while integrating quantum computing selectively.
How to Practice
- Benchmark millions of users and billions of transactions to ensure reliability.
- Design quantum integration only for peak-scale operations, keeping the majority of workloads classical.
Examples
- Festival Sale Traffic Handling: Keep standard operations on classical systems and trigger quantum-based route optimization for delivery logistics only.
- Inventory Restocking Decisions: Classical cloud handles everyday stock, quantum computes complex multi-warehouse allocations for large-scale campaigns.
Outcome: Enterprises maintain high reliability and SLA adherence, while quantum is invoked only when necessary.
Phase 6: Enterprise Value Governance (E)
Goal: Govern quantum usage with clear ROI, cost, and compliance frameworks.
How to Practice
- Implement dashboards that track cost vs benefit for quantum workloads.
- Define ROI thresholds and compliance approvals to ensure value-driven quantum adoption.
Examples
- Cost-Benefit Analysis for Delivery Optimization: Only trigger quantum computations when expected cost savings exceed operational thresholds.
- Regulatory Compliance Checks: Use governance frameworks to approve quantum simulations for inventory or pricing adjustments across regions.
Outcome: Quantum adoption is board-safe and value-driven, mitigating risk and ensuring measurable business impact.
Conclusion
By practicing Q-SCALE phase-wise, e-commerce enterprises can evolve from cloud-native AI operations to quantum-ready platforms without disruption.
Key Takeaways:
- Quantum is an accelerator, not a replacement for cloud or AI.
- Security, orchestration, and governance are foundational enablers.
- Talent and algorithm readiness are critical for adoption success.
- Business value remains the ultimate driver for quantum deployment.
This structured approach transforms the abstract concept of quantum computing into practical, actionable steps that CXOs, enterprise architects, and IT teams can implement today.
